Back to my homepage
Accepted by IEEE TPAMI 2021
Revisiting Light Field Rendering with Deep Anti-Aliasing Neural Network
Gaochang Wu1, Yebin Liu2, Lu Fang2, Tianyou Chai1
1. Northeastern University, 2. Tsinghua University
Abstract
The light field (LF) reconstruction is mainly confronted with two challenges, large disparity and non-Lambertian effect. Typical approaches either address the large disparity challenge using depth estimation followed by view synthesis or eschew explicit depth information to enable non-Lambertian rendering, but rarely solve both challenges in a unified framework. In this paper, we revisit the classic LF rendering framework to address both challenges by incorporating it with advanced deep learning techniques. First, we analytically show that the essential issue behind the large disparity and non-Lambertian challenges is the aliasing problem. Classic LF rendering approaches typically mitigate the aliasing with a reconstruction filter in the Fourier domain, which is, however, intractable to implement within a deep learning pipeline. Instead, we introduce an alternative framework to perform anti-aliasing reconstruction in the image domain and prove in theory the comparable and even superior efficacy on the aliasing issue. To explore the full potential, we then embed the anti-aliasing framework into a deep neural network through the design of an integrated architecture and trainable parameters. The network is trained through end-to-end optimization using a peculiar training set, including regular LFs and unstructured LFs. The proposed deep learning pipeline shows a substantial superiority on solving both the large disparity and the non-Lambertian challenges compared with other state-of-the-art approaches. In addition to the view interpolation for a LF, we also show that the proposed pipeline also benefits light field view extrapolation.
[Interpolation Video] [Extrapolation Video] [Code]
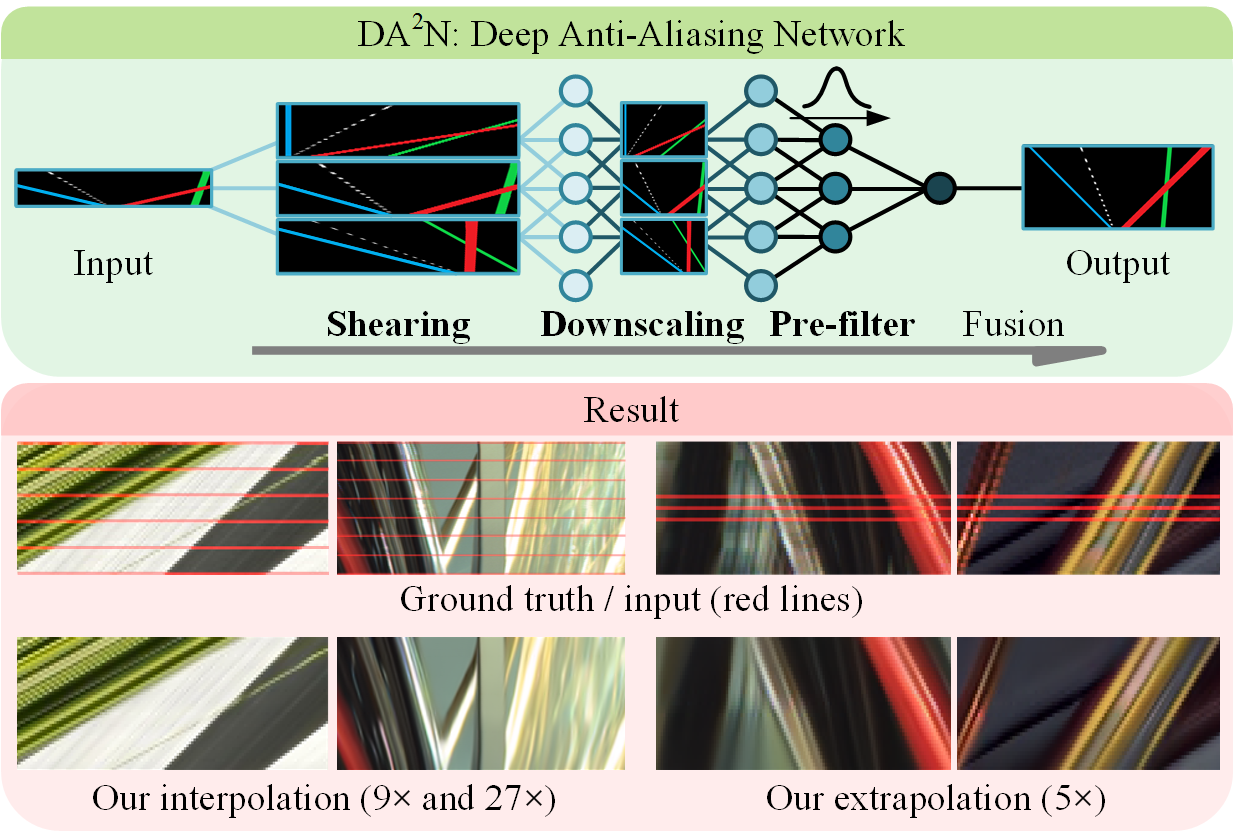
Fig 1. Schematic diagram of the proposed Deep Anti-Aliasing Network (DA2N) with embedding shearing, downscaling and prefiltering. In the result, we use input views indicated by the red lines for the EPI reconstruction, including interpolation and extrapolation.
Network
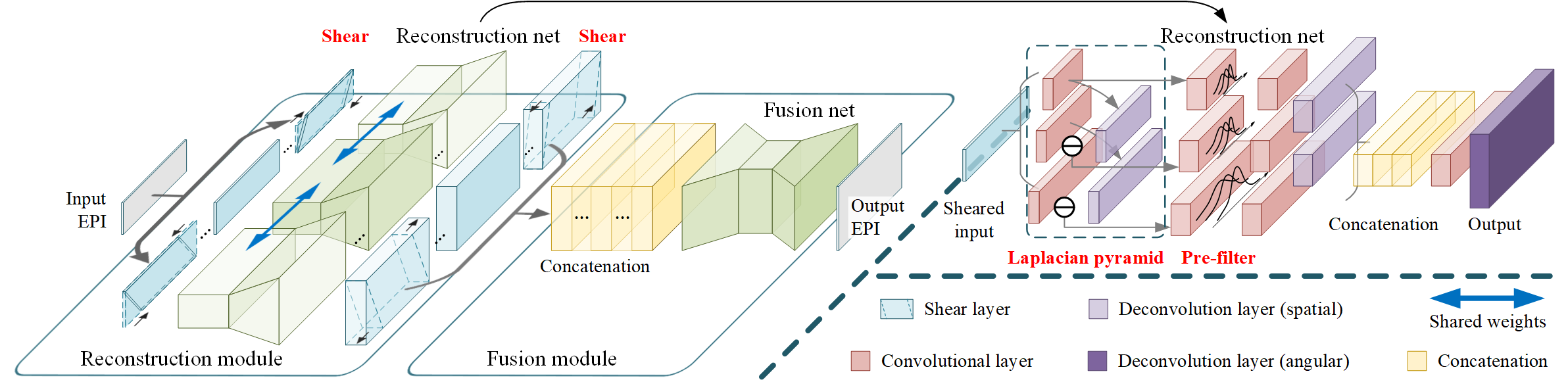
Fig 2. Architecture of the proposed deep anti-aliasing network (DA2N) based on shearing, downscaling and prefiltering.
Results

Fig 3. Comparison of the results (x16 upsampling) on the LFs from the ICME DSLF dataset.
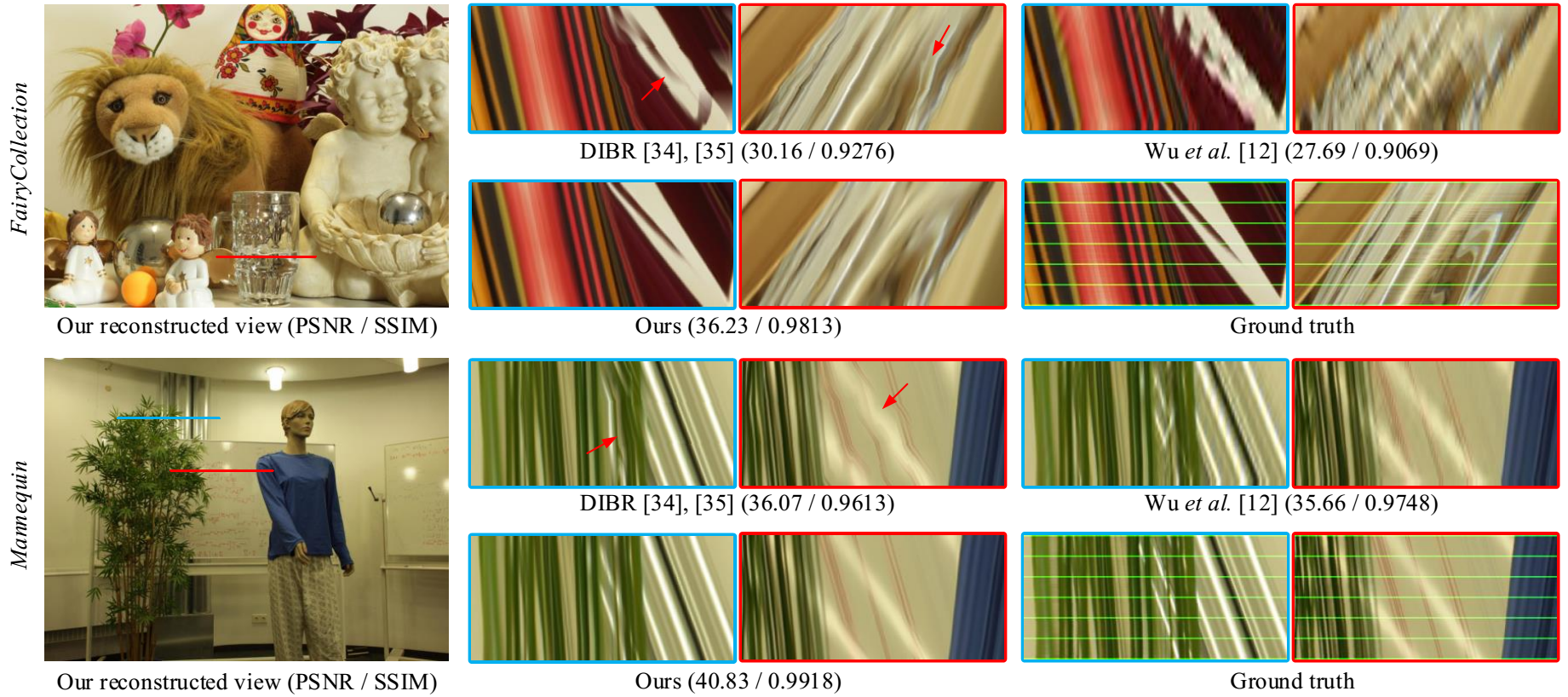
Fig 4. Comparison of the results (16x upsampling) on the light fields from the MPI Light Field Archive.
Technical Paper
Supplemental Material
Citation
Gaochang Wu, Yebin Liu, Lu Fang, Tianyou Chai. "Revisiting Light Field Rendering with Deep Anti-Aliasing Neural Network," IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, to be published
@article{wu2021revisiting,
title={Revisiting Light Field Rendering with Deep Anti-Aliasing Neural Network},
author={Gaochang Wu and Yebin Liu and Lu Fang and Tianyou Chai},
year={to be published},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence}
}